REST 客户端
Admin-on-rest可以与任何rest服务器通信而不考虑它使用的 REST dialect。 无论是JSON API, HAL, OData或者一个自定义dialect,Admin-on-rest唯一需要的就是一个 REST client 函数。这个地方是来转换REST请求到HTTP请求和HTTP响应到REST响应。
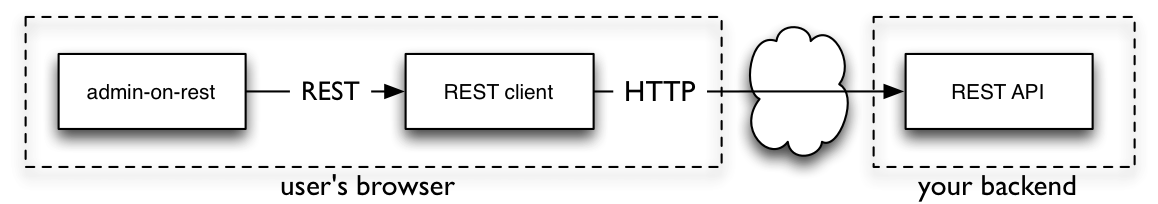
<Admin>组件的restClient参数必须是一个具有如下签名的函数:
/**
* Execute the REST request and return a promise for a REST response
*
* @example
* restClient(GET_ONE, 'posts', { id: 123 })
* => Promise.resolve({ data: { id: 123, title: "hello, world" } })
*
* @param {string} type Request type, e.g GET_LIST
* @param {string} resource Resource name, e.g. "posts"
* @param {Object} payload Request parameters. Depends on the action type
* @returns {Promise} the Promise for a REST response
*/
const restClient = (type, resource, params) => new Promise();
你会发现一个实现了REST client的例子在src/rest/simple.js;
restClient也是在这个理想的地方来添加HTTP头,身份验证,等等。
可用客户端
Admin-on-rest默认提供了两个REST客户端:
- simpleRestClient主要服务作为一个例子。顺便说一下,它是与FakeRestAPI兼容。
- JSON server:jsonServerRestClient
你可以在第三方的仓库中为admin-on-rest找到更多REST客户端:
- Feathersjs:josx/aor-feathers-client
- Firebase:sidferreira/aor-firebase-client
- GraphQL:marmelab/aor-simple-graphql-client (使用Apollo)
- JSON API:moonlight-labs/aor-jsonapi-client
- Local JSON:marmelab/aor-json-rest-client。它甚至不使用HTTP。 用于测试目的。
- Loopback: kimkha/aor-loopback
- Parse Server: leperone/aor-parseserver-client
- PostgREST: tomberek/aor-postgrest-client
如果您为另一个后端编写了REST客户端,并开放源代码,请完善此列表具有您的软件包。
简易的REST客户端
这个REST客户端适合API使用简单 GET 参数进行筛选和排序。这个dialect适用于例如在FakeRest中。
| REST verb | API calls |
|---|---|
GET_LIST |
GET http://my.api.url/posts?sort=['title','ASC']&range=[0, 24]&filter={title:'bar'} |
GET_ONE |
GET http://my.api.url/posts/123 |
CREATE |
POST http://my.api.url/posts/123 |
UPDATE |
PUT http://my.api.url/posts/123 |
DELETE |
DELETE http://my.api.url/posts/123 |
GET_MANY |
GET http://my.api.url/posts?filter={ids:[123,456,789]} |
GET_MANY_REFERENCE |
GET http://my.api.url/posts?filter={author_id:345} |
注意: 这个简易的REST客户端期望API在响应 GET_LIST 调用中包含一个Content-Range头。该值必须是集合中的资源总数。这使 admin-on-rest 能够知道总共有多少页资源,并生成分页控件。
Content-Range: posts 0-24/319
在JS代码中如果您的API是在另一个域中,你需要到白名单中为这个头添加一个Access-Control-Expose-Headers CORS 头。
Access-Control-Expose-Headers: Content-Range
这里是如何在你的admin中用它:
// in src/App.js
import React from 'react';
import { simpleRestClient, Admin, Resource } from 'admin-on-rest';
import { PostList } from './posts';
const App = () => (
<Admin restClient={simpleRestClient('http://path.to.my.api/')}>
<Resource name="posts" list={PostList} />
</Admin>
);
export default App;
JSON Server REST客户端
此REST客户端适合API由JSON Server驱动比如 JSONPlaceholder。
| REST verb | API calls |
|---|---|
GET_LIST |
GET http://my.api.url/posts?_sort=title&_order=ASC&_start=0&_end=24&title=bar |
GET_ONE |
GET http://my.api.url/posts/123 |
CREATE |
POST http://my.api.url/posts/123 |
UPDATE |
PUT http://my.api.url/posts/123 |
DELETE |
DELETE http://my.api.url/posts/123 |
GET_MANY |
GET http://my.api.url/posts/123, GET http://my.api.url/posts/456, GET http://my.api.url/posts/789 |
GET_MANY_REFERENCE |
GET http://my.api.url/posts?author_id=345 |
注意: 这个jsonServer REST客户端期望在响应GET_LIST调用中包含一个X-Total-Count头。该值必须是集合中的资源总数。这使admin-on-rest能够知道总共有多少页资源,并生成分页控件。
X-Total-Count: 319
在JS代码中如果您的API是在另一个域中,你需要到白名单中为这个头添加一个Access-Control-Expose-HeadersCORS 头。
Access-Control-Expose-Headers: X-Total-Count
这里是如何在你的admin中用它:
// in src/App.js
import React from 'react';
import { jsonServerRestClient, Admin, Resource } from 'admin-on-rest';
import { PostList } from './posts';
const App = () => (
<Admin restClient={jsonServerRestClient('http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com')}>
<Resource name="posts" list={PostList} />
</Admin>
);
export default App;
添加自定义头
simpleRestClient和jsonServerRestClient函数都接受http client函数作为第二个参数。默认情况下, 他们使用admin-on-rest的fetchUtils.fetchJson()作为http client。它类似于HTML5的fetch(),除了它会自动处理json解码和http错误代码。
这意味着如果你需要添加自定义头到你的请求中,你只需封装这个fetchJson()回调在你自己的函数内部:
import { simpleRestClient, fetchUtils, Admin, Resource } from 'admin-on-rest';
const httpClient = (url, options = {}) => {
if (!options.headers) {
options.headers = new Headers({ Accept: 'application/json' });
}
// add your own headers here
options.headers.set('X-Custom-Header', 'foobar');
return fetchUtils.fetchJson(url, options);
}
const restClient = simpleRestClient('http://localhost:3000', httpClient);
render(
<Admin restClient={restClient} title="Example Admin">
...
</Admin>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
现在所有到REST API请求都将包含X-Custom-Header: foobar头。
提示:自定义头的最常见用法是进行身份验证。fetchJson已经将Authorization令牌头作为基础支持:
const httpClient = (url, options) => {
options.user = {
authenticated: true,
token: 'SRTRDFVESGNJYTUKTYTHRG'
}
return fetchUtils.fetchJson(url, options);
}
现在对REST API的所有请求都将包含Authorization: SRTRDFVESGNJYTUKTYTHRG头。
装饰你的REST客户端(文件上传的例子)
您可以在给定的资源上增强其功能而不是编写自己的REST client或使用第三方的REST client。例如,如果您想要使用上传组件(如<ImageInput />组件),你可以按以下方式修饰它:
/**
* Convert a `File` object returned by the upload input into
* a base 64 string. That's easier to use on FakeRest, used on
* the ng-admin example. But that's probably not the most optimized
* way to do in a production database.
*/
const convertFileToBase64 = file => new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.readAsDataURL(file);
reader.onload = () => resolve(reader.result);
reader.onerror = reject;
});
/**
* For posts update only, convert uploaded image in base 64 and attach it to
* the `picture` sent property, with `src` and `title` attributes.
*/
const addUploadCapabilities = requestHandler => (type, resource, params) => {
if (type === 'UPDATE' && resource === 'posts') {
if (params.data.pictures && params.data.pictures.length) {
// only freshly dropped pictures are instance of File
const formerPictures = params.data.pictures.filter(p => !(p instanceof File));
const newPictures = params.data.pictures.filter(p => p instanceof File);
return Promise.all(newPictures.map(convertFileToBase64))
.then(base64Pictures => base64Pictures.map(picture64 => ({
src: picture64,
title: `${params.data.title}`,
})))
.then(transformedNewPictures => requestHandler(type, resource, {
...params,
data: {
...params.data,
pictures: [...transformedNewPictures, ...formerPictures],
},
}));
}
}
return requestHandler(type, resource, params);
};
export default addUploadCapabilities;
这样,您可以简单地使用你的upload-capable客户端到你的app调用此装饰:
import jsonRestClient from 'aor-json-rest-client';
import addUploadFeature from './addUploadFeature';
const restClient = jsonRestClient(data, true);
const uploadCapableClient = addUploadFeature(restClient);
render(
<Admin restClient={uploadCapableClient} title="Example Admin">
// [...]
</Admin>,
document.getElementById('root'),
);
编写你自己的REST客户端
很多时候,没有一个核心的REST客户端完全匹配你的API。在这种情况下,您不得不编写自己的REST客户端。但不要害怕,这很容易!
请求格式
REST请求必需要一个type(例如:GET_ONE),一个resource(例如:'posts')和一组parameters。
提示:相比之下, HTTP 请求需要一个动词(例如:‘GET’), 一个 url(例如: ‘http://myapi.com/posts’),一系列 headers(🐘 Content-Type)和一个 body。
可能的类型是:
| Type | Params format |
|---|---|
GET_LIST |
{ pagination: { page: {int} , perPage: {int} }, sort: { field: {string}, order: {string} }, filter: {Object} } |
GET_ONE |
{ id: {mixed} } |
CREATE |
{ data: {Object} } |
UPDATE |
{ id: {mixed}, data: {Object} } |
DELETE |
{ id: {mixed} } |
GET_MANY |
{ ids: {mixed[]} } |
GET_MANY_REFERENCE |
{ target: {string}, id: {mixed}, pagination: { page: {int} , perPage: {int} }, sort: { field: {string}, order: {string} }, filter: {Object} } |
例子:
restClient(GET_LIST, 'posts', {
pagination: { page: 1, perPage: 5 },
sort: { field: 'title', order: 'ASC' },
filter: { author_id: 12 },
});
restClient(GET_ONE, 'posts', { id: 123 });
restClient(CREATE, 'posts', { title: "hello, world" });
restClient(UPDATE, 'posts', { id: 123, { title: "hello, world!" } });
restClient(DELETE, 'posts', { id: 123 });
restClient(GET_MANY, 'posts', { ids: [123, 124, 125] });
restClient(GET_MANY_REFERENCE, 'comments', {
target: 'post_id',
id: 123,
sort: { field: 'created_at', order: 'DESC' }
});
响应格式
REST响应是对象。格式取决于类型。
| Type | Response format |
|---|---|
GET_LIST |
{ data: {Record[]}, total: {int} } |
GET_ONE |
{ data: {Record} } |
CREATE |
{ data: {Record} } |
UPDATE |
{ data: {Record} } |
DELETE |
{ data: {Record} } |
GET_MANY |
{ data: {Record[]} } |
GET_MANY_REFERENCE |
{ data: {Record[]}, total: {int} } |
{Record}是一个至少具有id属性的对象字面量,例如:{ id: 123, title: "hello, world" }。
例子:
restClient(GET_LIST, 'posts', {
pagination: { page: 1, perPage: 5 },
sort: { field: 'title', order: 'ASC' },
filter: { author_id: 12 },
})
.then(response => console.log(response));
// {
// data: [
// { id: 126, title: "allo?", author_id: 12 },
// { id: 127, title: "bien le bonjour", author_id: 12 },
// { id: 124, title: "good day sunshine", author_id: 12 },
// { id: 123, title: "hello, world", author_id: 12 },
// { id: 125, title: "howdy partner", author_id: 12 },
// ],
// total: 27
// }
restClient(GET_ONE, 'posts', { id: 123 })
.then(response => console.log(response));
// {
// data: { id: 123, title: "hello, world" }
// }
restClient(CREATE, 'posts', { title: "hello, world" })
.then(response => console.log(response));
// {
// data: { id: 450, title: "hello, world" }
// }
restClient(UPDATE, 'posts', { id: 123, { title: "hello, world!" } })
.then(response => console.log(response));
// {
// data: { id: 123, title: "hello, world!" }
// }
restClient(DELETE, 'posts', { id: 123 })
.then(response => console.log(response));
// {
// data: { id: 123, title: "hello, world" }
// }
restClient(GET_MANY, 'posts', { ids: [123, 124, 125] })
.then(response => console.log(response));
// {
// data: [
// { id: 123, title: "hello, world" },
// { id: 124, title: "good day sunshise" },
// { id: 125, title: "howdy partner" },
// ]
// }
restClient(GET_MANY_REFERENCE, 'comments', {
target: 'post_id',
id: 123,
sort: { field: 'created_at', order: 'DESC' }
});
.then(response => console.log(response));
// {
// data: [
// { id: 667, title: "I agree", post_id: 123 },
// { id: 895, title: "I don't agree", post_id: 123 },
// ],
// total: 2,
// }
错误格式
当REST API返回一个错误时,这个rest客户端应该抛出 一个 Error 对象。这个对象应该包含一个具有HTTP 响应代码(404,500,等等)的status属性。Admin-on-rest检查这个错误代码并将其用于身份验证(在401或403错误的情况下)
示例实现
查看来自simple REST client中的代码:它是一个好的开始来达到一个自定义的rest client实现。